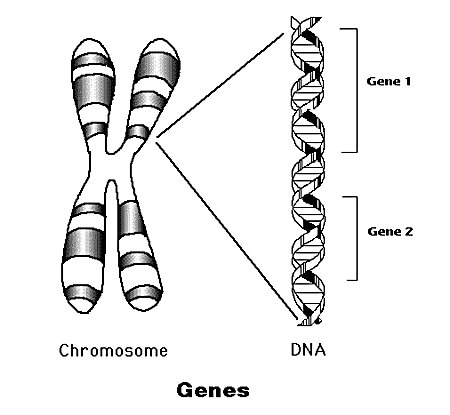
| DNA
AND GENES
Many
people might think that what is the link between Brahmins, DNA and
Genes as it is a part of medical science but, the fact is that DNA
and Genes has everything got to do with what we are today.
Just take a simple example that if a person comes near you and asks that :
The
answer to these entire questions is simple and can be explained
through the concept of DNA and Genes which is explained in detail
below.
DNA
:
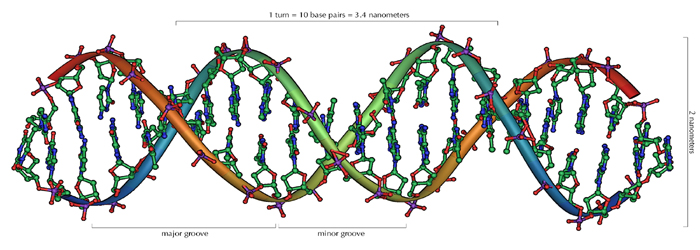
Deoxyribonucleic
Acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions
used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms
and some viruses.
The
main role of DNA molecules is the long-term storage of information.
DNA is often compared to a set of blueprints or a recipe, or a
code, since it contains the instructions needed to construct other
components of cells, such as proteins and RNA molecules. The DNA
segments that carry this genetic information are called genes,
but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved
in regulating the use of this genetic information.
Chemically,
DNA consists of two long polymers of simple units called nucleotides,
with backbones made of sugars and phosphate groups joined by ester
bonds. These two strands run in opposite directions to each other
and are therefore anti-parallel. Attached to each sugar is one
of four types of molecules called bases. It is the sequence of
these four bases along the backbone that encodes information.
This information is read using the genetic code, which specifies
the sequence of the amino acids within proteins. The code is read
by copying stretches of DNA into the related nucleic acid RNA,
in a process called transcription.
Within
cells, DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes. These
chromosomes are duplicated before cells divide, in a process called
DNA replication. Eukaryotic organisms (animals, plants, fungi,
and protists) store their DNA inside the cell nucleus, while in
prokaryotes (bacteria and archae) it is found in the cell's cytoplasm.
Within the chromosomes, chromatin proteins such as histones compact
and organize DNA. These compact structures guide the interactions
between DNA and other proteins, helping control which parts of
the DNA are transcribed.
The History of DNA Research :
The
history of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) research begins with Friedrich
Miescher, a Swiss biologist who in 1868 carried out the first
carefully thought out chemical studies on the nuclei of cells.
Using the nuclei of pus cells obtained from discarded surgical
bandages, Miescher detected a phosphorus-containing substance
that he named nuclein. He showed that nuclein consists of an acidic
portion, which we know today as DNA, and a basic protein portion
now recognized as histones, a class of proteins responsible for
the packaging of DNA. Later he found a similar substance in the
heads of salmon sperm cells. Although he separated the nucleic
acid fraction and studied its properties, the covalent structure
of DNA did not become known with certainty until the late 1940's.
From
these very important early experiments, and a wealth of other
corroborating evidence, it is now certain that DNA is the carrier
of genetic information in all living cells.
Characteristics of DNA : Double
helix, five-carbon sugar deoxyribose, a phosphate group, hold
genetic information, anti parallel, held by hydrogen bonds.
Four
Bases of DNA: Cytosine, Adenine, Guanine, and Thymine.
Four
Bases of RNA: Uracil, Cytosine, Adenine, and Guanine.
Uracil
replaces Thymine in RNA.
Y-DNA : Y-DNA
is passed from father to son unchanged for upwards to 20 or more
generations. It is particularly useful in proving or disproving
a relationship when the documentation is not provable. Y-DNA can
also help discover links to family lines that document research
has not uncovered.
MTDNA : MTDNA
(mitochondrial DNA) is not as useful as is Y-DNA. It is passed
from mother to child unchanged for thousands of years, but since
a females surname changes with marriage, it isn't as useful in
tracing family lines.
The
human body consists of 60 thousand billion cells (e.g. white blood
cells, muscle cells, or cheek cells) of which nearly every single
cell contains our entire genetic information, the DNA. Inside
the cell, DNA is found inside the nucleus (chromosomal DNA, consisting
of autosomal DNA, X chromosomal DNA and Y chromosomal DNA) and
outside the nucleus (mitochondrial DNA).
Our
autosomal DNA is inherited from both parents, but Y-chromosomal
DNA (Y-DNA) is inherited only from father to son, and mitochondrial
DNA (MTDNA) is inherited only from our mother.
The
original Y chromosome has mutated its DNA naturally over the generations
and these new Y types have settled in various parts of the world
in prehistory. By determining your present Y-type and searching
the worldwide Y database, Roots for Real can give you a good idea
where in the world your father's lineage is generally found today.
Additionally,
family researchers (genealogists) who wish to know whether two
people with the same surname are related are increasingly using
Y chromosomal tests. This is possible because in many cultures,
family names or surnames are passed down by the father just like
the Y chromosome.
In
such cases, two Y tests are needed: one Y test for oneself, and
Y test for the person with the same surname who is suspected to
be related. All that is then needed is to compare whether the
two Y results are identical.
The
use of DNA testing for determining a person's ancestry is becoming
more and common. By linking your maternal DNA (mitochondrial DNA)
and your paternal DNA (the y-chromosome), these ancestry databases
are effectively able to link you to other people to whom you may
be related and thereby determining to some degree your ancestral
lineage and where your ancestors came from.
DNA
Ancestry Testing - Y-Chromosome and Mitochondial DNA.
The
first thing that genealogists look for is a father-to-son linkage,
tracked down the Y chromosome which only men posses. Therefore,
they are able to observe the Y chromosome that appears in other
people and compare them, to determine where a paternal link may
be present.
This
comparison, in essence, allows for the genealogist to try and
find paternal linkages amongst people. The other thing that can
be done is to link maternal DNA. This in particular is a very
powerful testing method that allows for accurate tracking back
over many generations because of the mitochondria.
Unlike
DNA found in the nucleus, which can be altered and changes as
environments change, mitochondrial DNA is a direct connection
from child to mother that can't be altered along the way. By taking
a sample of the mitochondrial DNA, which is different than the
DNA found in the nucleus, the genealogist can determine a maternal
linkage. By taking this information, they can, once again, find
perhaps those long lost cousins or celebrity ancestors.
One
look around a room tells you that each person has slight differences
in their physical make up and therefore in their DNA. These subtle
variations in DNA are called polymorphisms (literally "many
forms"). Many of these gene polymorphisms account for slight
differences between people such as hair and eye color. But some
gene variations may result in disease or an increased risk for
disease. Although all polymorphisms are the result of a mutation
in the gene, geneticists only refer to a change as a mutation
when it is not part of the normal variations between people.
Genes
:
Genes
are working subunits of DNA. Genes or genetics are what are
passed down biologically through the generations of your family.
They determine everything from your physical appearance to even
diseases you may inherit.
A
gene is the unit of heredity and carries inherited information.
Genes interact with each other to influence physical development
and behavior. Genes consist of a long strand of DNA (RNA in
some viruses) that contains a promoter, which controls the activity
of a gene, and a coding sequence, which determines what the
gene produces. When a gene is active, the coding sequence is
copied in a process called transcription, producing a RNA copy
of the gene's information. This RNA can then direct the synthesis
of proteins via the genetic code. However, RNA's can also be
used directly, for example as part of the ribosome. These molecules
resulting from gene expression whether RNA or protein are known
as gene products.
Each
gene has a special job to do. It carries blueprints - the instructions
- for making proteins (say: pro-teens) in the cell. Proteins are
the building blocks for everything in your body. Bones and teeth,
hair and earlobes, muscles and blood, all are made up of proteins
(as well as other stuff). Those proteins help our bodies grow,
work properly, and stay healthy. Scientist's today estimate that
each gene in the body may make as many as 10 different proteins.
That's over 300,000 proteins!
Like
chromosomes, genes come in pairs. Each of your biological parents
has two copies of each of their genes, and each parent passes
along just one copy to make up the genes you have. Genes that
are passed on to you determine many of your traits, such as your
hair color and skin color.
The
existence of genes was first suggested by Gregor Mendel (1822-1884),
who, in the 1860s, studied inheritance in peaplants and hypothesized
a factor that conveys traits from parent to offspring. He spent
over 10 years of his life on one experiment.
Genes
are actually a subset of a cell's DNA. While all of your genes
are made of DNA, your entire DNA is not composed of genes. In
fact, less than two percent of a person's DNA represents active
genes! The rest of the DNA seems to be involved mediating how
the genes are expressed.
Deoxyribonucleic
Acid is found as long chains with each "link" called
a nucleotide. The structure of DNA is the well known double helix.
Each bacterial cell generally contains a single chain of duplex
DNA, called a chromosome, with about five million links in it.
By comparison, cells in human beings contain 2 copies of 23 different
chromosomes with around 100 million nucleotides each.
Genes
were classically defined as the fundamental units of inheritance.
Today we understand genes to be portions of DNA that contain the
information needed by cells to live. In particular, genes are
special sequences of nucleotides that are used to design proteins
which carry out the work of building, maintaining, and reproducing
the cell.
Some
of the implications of genetic uniformity by marrying cousins
are :
1.
Less genetic diversity within the village population,
2. Less selective advantage, 3. Harmful genes will be exposed, 4. Smaller circle of courtship, 5. Inbreeding depression, 6. Reduction in vigor and, 7. Less resistance to diseases. Genetic defect : Father
with Abnormal autosomal chromosome. Mother with Normal gene on
autosomal chromosome.
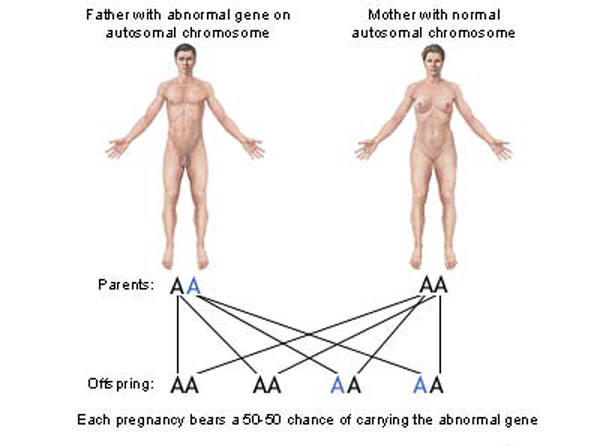
Here, A
means Normal and A means Abnormal.
According
to the graph given above each pregnancy bears a 50 - 50 chance
of carrying the abnormal gene.
From
the above given scientific research we can understand the concept
of DNA and Genes. This concept was also known by the Rishis and
hence they kept certain guide lines for marriage such as to strictly
avoid marriage between same gotras, to check if there is any physical
or mental defect in any person of the family who the son or daughter
is getting married to.
Our
ancestors knew this concept but some how we are not able to medically
prove it because of the lack of medical science but now as the
forensics has developed and through the help of it we can prove
it that Lord Brahma and our Ancestors DNA is in us.
How
to make DNA strong :
There
are 2 concepts by which a person can make his/her DNA strong.
Pure
food gives rise to pure thoughts. If one wants to have a strong
DNA and become a devotee then meat should be renounced. This is
because it makes excitement and then its nature is impure.
It
is not proper for us to take another life for our personal enjoyment.
By eating animals man gets an animalistic nature and thus brings
about the destruction of the race.
A
person should also avoid smoking cigarettes, drinking and non-vegetarian
food and should have regular good eating and sleeping habits,
should live in healthy environment and daily exercise to make
DNA stronger.
The
more our DNA is strong the stronger will be our coming generations.
|
||||||||||||||||||